Connecting to a database
You can either connect to your database from the Celonis Platform directly or use an uplink connection, for when you don't want to or can't allow direct access.
This connection type depends on the database you are attempting to connect to.
Prerequisites for connecting to databases
In order to extract from a database, you need to create or use an existing user who has read (SELECT) access to all tables that should be extracted.
The user should also access the schema information_schema to read metadata for the tables to be extracted.
For more information about this, consult your database's official documentation.
Before creating a connection between your database and the Celonis Platform you must decide which connection type you use.
Direct connections to the database
Use this when you want to allow the Celonis Platform to directly access your database.
Uplink connections to the database via an on-premise extractor
Use this when you don't want to or can't allow the Celonis Platform to directly access your database. The connection between the database and Celonis is then established using an on-premise extractor that's installed within your network and ideally on a dedicated server.
The role of the extractor is to poll and fetch job requests from the Celonis Platform, before then submitting the execution information the the database via an SQL query. Once the data is retrieved from the database, the extractor feathces it and sends it back to the Celonis Platform. As such, the connection between the database and the Celonis Platform is always made by the extractor, with it continuously querying the Celonis Platform for any extractions to execute.
For more information about the on-premise extractor (including system requirements), see: On-premise extractors.
For the database extractor to communicate with your database and the Celonis Platform, you must modify your network settings to allow access.
The settings here are based on the connection type you defined in step 1:
Network settings for direct connections
The following network settings apply only for direct connections:
Source system | Target system | Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Celonis Platform | Source system | Depending on the database, typical ports are 5432 for PostgreSQL and 30015 for HANA for example | TCP | JDBC connection from the Celonis Platform to the database. The port is the one you normally use to connect to the database. The IPs of the Celonis Platform depending on the cloud cluster (which can be seen in the URL). |
Network settings for uplink connections
The following network settings apply only for uplink connections (via the on-premise extractor):
Source system | Target system | Port | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
On-premise extractor server | Source system | Depending on the database, typical ports are 5432 for PostgreSQL and 30015 for HANA for example. | TCP | JDBC connection from on-premise extractor server to the database. The port is the one you normally use to connect to the database. |
On-premise extractor server | Celonis Platform | 443 | TCP | HTTPS connection from on-premise extractor server to Celonis cloud endpoint. The IPs of the Celonis Platform depending on the cloud cluster (which can be seen in the URL). |
Celonis Platform IP addresses depending on the cluster
The respective clusters use multiple IPs each, so you need to enable all three of them in your firewall configuration to connect the on-premise extractor server and the cloud endpoint.
For a complete list of inbound and outbound Celonis Platform IP addresses to be allowlisted if needed, see: Allowlisting Celonis domain names, IP addresses, and third-party domains
Note
This step is only needed if your database is not reachable from the Celonis Platform.
For this step, you need to set up the database extractor in your network if your database is not reachable from the Celonis Platform.
For more information, see: Setting up
If you would like to use a proxy (optional), see: Proxy settings for on-premise extractors.
You can now create the connection between your database and the Celonis Platform from your data pool diagram:
Click Data Connections.
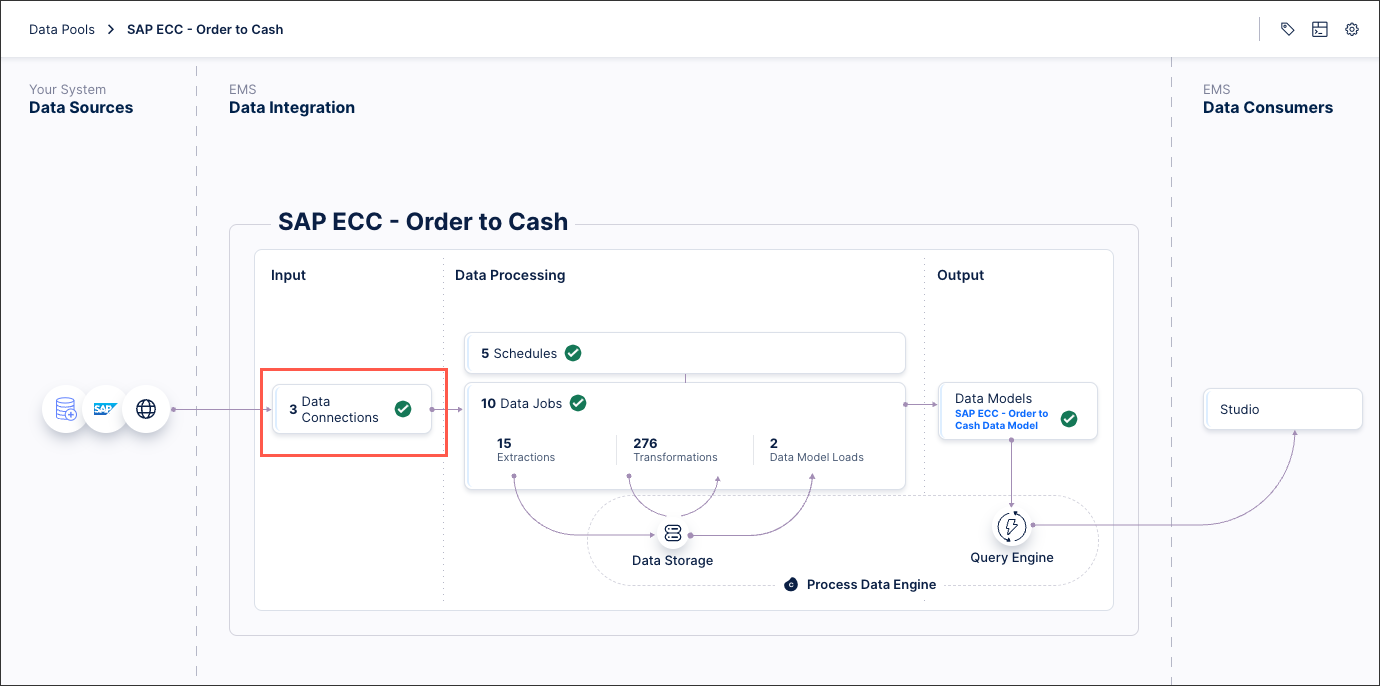
Click Add Data Connection and select Connect to Data Source.
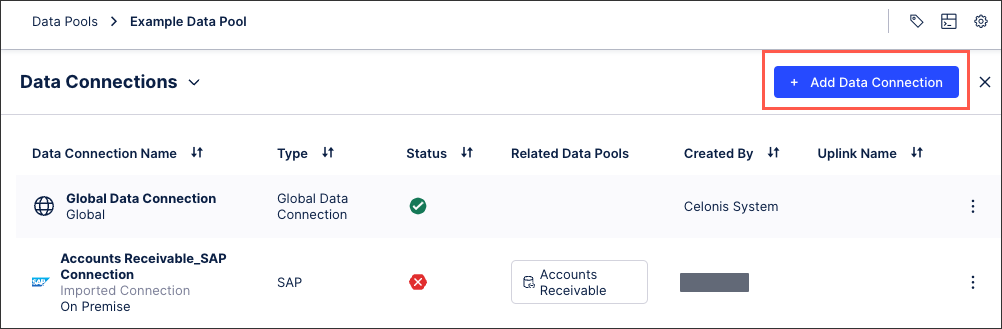
For direct connections, select Cloud - Database.
For uplinked connections, select: On-Premise - Database and then select your uplink (configured as part of step 1).
Configure the following connection details, with the options here depending on your choice of uplinked or direct connection:
Name: An internal reference for the data connection.
Uplink Connections: The name of the Uplink Extractor Server installed on your end.
Database Type: The type (generic name) of the database to which you want to connect.
Configuration type: Select Standard.
Host: The database server name or IP address of the database server.
Port: The port to connect to the database server.
Service Name: If applicable to a specific database type (e.g. Oracle), enter the Service Name (Alias) associated with the database server.
Schema name: The schema to use (optional).
Additional Properties: Additional properties like validateCertificate=false for a HANA database or integratedSecurity=true for domain users in MSSQL.
Username and password: The database credentials used by the user.
Maximum number of parallel extractions: This is usually governed by the database type you are using. The default value chosen is 4.
Timeout for database connections: Timeout for all database connections created in this connection (specific to this connection only). This value will overwrite the local timeout (in application.yaml) in case of uplinked connection.
Click Test Connection and correct any highlighted issues.
Click Save.
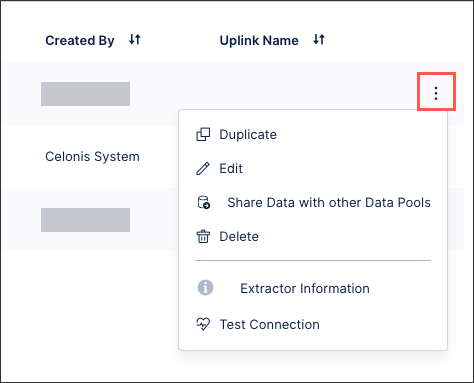
The connection between your Cloudera Impala account and the Celonis Platform is established. You can manage this connection at any time by clicking Options:
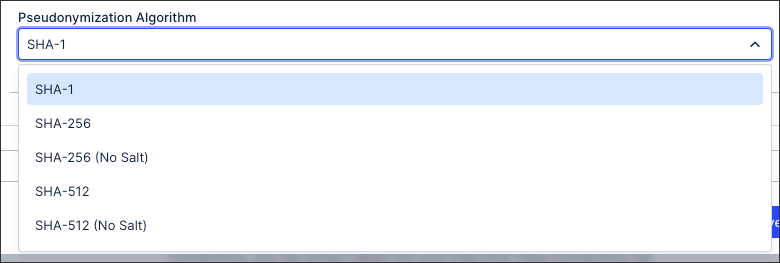
As part of the advanced settings for data connections, you can pseudonymiz the data you extract using SHA-1, SHA-256 (with and without salt), and SHA-512 (with and without salt) algorithms. If you select to pseudonymize your data, values as displayed in the source system will be replaced with hashed values.
Pseudonymization happens during the data extraction. Celonis requests source system data, then pseudonymizes that data upon receipt, converts it into parquet format, and then ingests this into the Celonis Platform.
 |