Knowledge Model - YAML Definitions
For advanced users, there is the option to define and configure Knowledge Models with YAML documents. YAML (“Yet Another Markup Language”) is a standardized, human-readable general-purpose markup language that provides a way to represent (describe and annotate) data.
Knowledge Model Meta Information
A Knowledge Model as represented in YAML consists of different segments. The first segment contains the required meta-information about the KM. The following modeling primitives are supported:
 |
Kind (required)
This segment is a single field that indicates whether the current Knowledge Model is an independent Knowledge Model ("BASE") or an extension of an existing Knowledge Model ("EXTENSION").
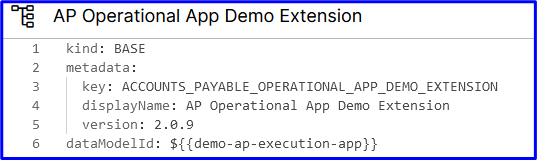
kind: BASE
Metadata (required)
The metadata segment contains information that is required for the processing and handling of the Knowledge Model by the Studio application, such as a unique key to reference the Knowledge Model and a human-readable display name.
Metadata: key: ACCOUNTS_PAYABLE_OPERATIONAL_APP_DEMO_EXTENSION displayName: AP Operational App Demo Extension version: 2.0.9
Data Model ID (required)
The Data Model ID is used to reference the data model which contains the underlying data. Inside the Data Model ID field, you can add the data model runtime variable using the ${{variable-key}} notation.
dataModelId: ${{demo-ap-execution-app}}For each Knowledge Model there can be only one Data Model at the same time. To gain data from multiple Data Models, you can either switch between Data Models with runtime Variables or use multiple Knowledge Models within a single view (one per component).
YAML Cheatsheet
For further information on YAML, check out the official website here.
YAML relies on indentation for structure, so correct indentation is very important.
Inline comments with a leading # are not supported in YAML. However, every Knowledge Model object has a field called
'internalNote'which can be used for documentation and comments. For example:kpis: - id: _open_invoices displayName: "# Open Invoices" description: Open Invoices internalNote: This is my documentation for complicated things which is not visible to business users. pql: COUNT(DISTINCT "RSEG"."_CASE_KEY")Scalars are defined using a colon and a space.
Examples:
id: OTD_KPI displayName: "On-Time Delivery KPI" order: 100
The preferred way to define lists of values is by Block Format (separating the list items by hyphens).
Example:
kpis: - id: OTD_KPI # remaining fields of the KPI definition - id: AUTOMATION_RATE_KPI # remaining fields of the KPI definition - id: REWORK_RATE_KPI # remaining fields of the KPI definition
Strings such as PQL statements can be denoted in five ways:
Plain Scalar
displayName: On-Time-Delivery
Attention: Plain scalar without (double) quotes can conflict with YAML syntax. Thus, it is highly encouraged to not use plain scalars for strings such as PQL statements.
Single Quoted (' ')
Single quotes in the string itself need to be escaped by doubling it (' is escaped as '')
displayName: 'On-Time-Delivery'
Double Quoted (" ")
Double quotes in the string itself need to be escaped using a backslash (" is escaped as \"). Furthermore, only double-quoted strings may contain escape sequences like \n for a new line.
displayName: "On-Time-Delivery"
Since double quotes are both YAML primitives and PQL primitives, you might encounter situations where the YAML parser has difficulty disambiguating double quotes correctly.
Literal Block Scalar (|)
The content of a literal block scalar starts after the pipe symbol in a new line and needs to be intended.
description: | This is a multiline text
Folded Block Scalar (>)
The content of a folded block scalar starts after the > sign
description: > This is a long line split into short lines
A Knowledge Model parses the PQL as written in the YAML with the following rules:
All new lines are rewritten as if they were single spaces
The YAML block is indented by 2 spaces
All new lines at the end are stripped
To learn more about multi-line YAML, check out https://yaml-multiline.info/