Validating KPIs for the case-centric Baseline Date Optimizer app
In the Baseline Date Optimizer app’s Knowledge Model, check that the KPIs (key performance indicators) contain the correct business logic for your organization. For the Baseline Date Optimizer app, you can manage the settings for most of the important KPIs using the Configuration view, but some KPIs can only be managed in the Knowledge Model.
The main Knowledge Model for the Baseline Date Optimizer app is “Baseline Date Optimizer - Knowledge Model”. Work with this Knowledge Model to validate and change KPIs. “Baseline Date Optimizer - Knowledge Model” points to the base Knowledge Model stored in the Celonis Marketplace, which you can’t update directly. Changes that you make to the PQL formulas, KPI names, or formatting in “Baseline Date Optimizer - Knowledge Model” override the base Knowledge Model.
Each KPI in a Knowledge Model contains a PQL (Process Query Language) formula. Some KPIs are reused inside other KPIs as nested formulas. When you adjust the business logic in a single formula, and save it, the change is simultaneously reflected in all the KPIs that reuse the formula.
You work with Knowledge Models in Studio, and any changes you make are applied when you publish a new version of the app. You’ll need Analyst permissions on Studio and the Knowledge Model to modify any of the KPIs and their calculations. If you need training, check out the training track “Build Knowledge Models and Views” on the Celonis Academy.
Here’s how to work with the KPIs in “Baseline Date Optimizer - Knowledge Model”:
In the Celonis navigation menu, select Studio.
Find the Baseline Date Optimizer app in your Studio space navigation.
Expand the package’s structure using the arrow.
Select “Baseline Date Optimizer - Knowledge Model”.
Select the KPIs section of the Knowledge Model.
You can sort and search the KPIs using their name or ID. The prefix to the ID shows what type of component they are. At the end of these instructions, we’ve noted the most important KPIs to check.
To see and edit the full PQL formula and other settings for a KPI, click its row to open an editor. The editor automatically validates any changes that you make in the PQL formula.
If you want a fuller-featured PQL editor that lets you select from the tables and columns in your data, click on the pen icon next to the PQL formula.
If you need to disable a KPI or formula, click the three vertical dots at the top of the editor, and select Disable Scope, then click Disable to confirm. When you do this, the object can't be accessed or used anywhere in the package, including by other apps that depend on it.
When you’ve made changes to the KPIs, use the Publish Package button at the top of the screen in your Studio space to publish a new version of the app.
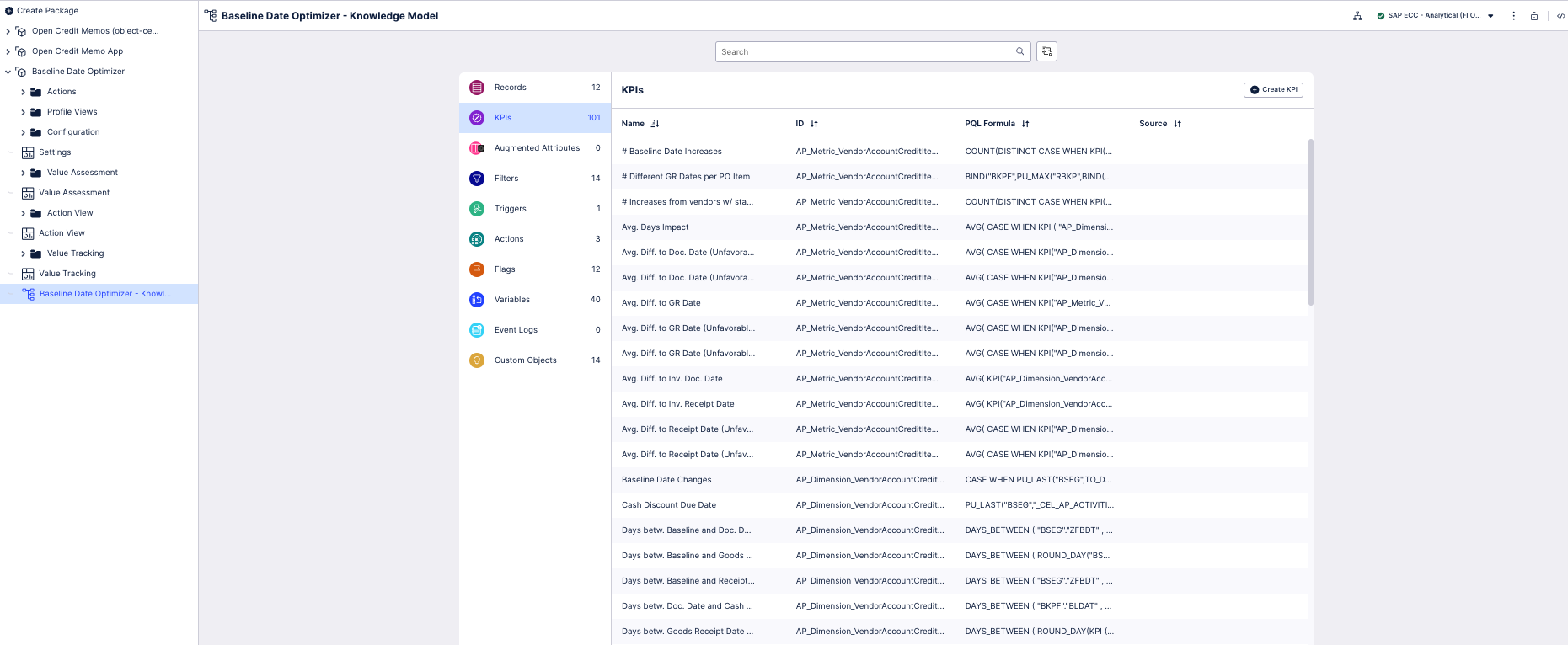
For the Baseline Date Optimizer app, many KPIs refer to runtime variables, especially for date fields, which you can configure in the Configuration View. In order to validate the business logic or potentially change it, you have to access the Knowledge Model.
To help you work with the KPIs in the Knowledge Model, we’ve grouped them into categories as follows:
App Scope
General Business Logic
Business Logic Cash Discount
Free Cash Flow Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Invoice Document Date
Cash Discount Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Invoice Document Date
Free Cash Flow Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Invoice Receipt Date
Cash Discount Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Invoice Receipt Date
Free Cash Flow Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Goods Receipt Date
Cash Discount Assessment for Baseline Date vs. Goods Receipt Date
Business Logic Action View
Business Logic Value Tracking
Use the Knowledge Model’s YAML editor in the “Final Model View” to see the KPIs listed by category. The KPIs for each category are listed below the category heading in the format “DO_NOT_USE_[categoryName].
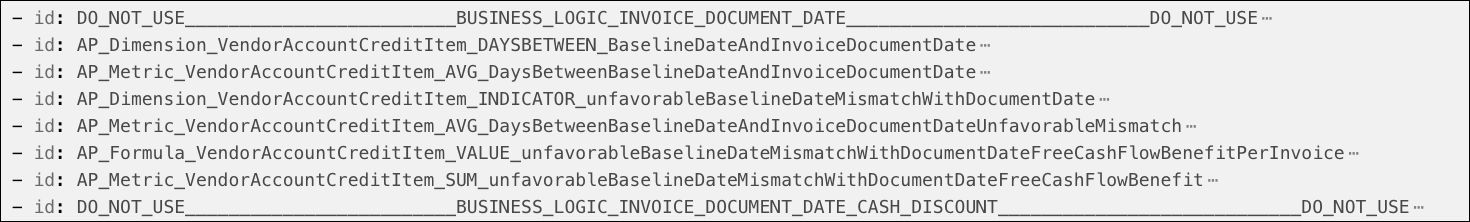
The Knowledge Model variable “Current Date” (with the ID AP_Variable_Input_CurrentDate) is relevant if you are analyzing a one-time extract of data taken in the past. The default setting is TODAY(), but if you set a fixed date on which the data extract was made, the validations and calculations are performed as if that date were today.