Knowledge Model - Variables (legacy views only)
Note
Legacy variables can only be used within this Knowledge Model. If you want to start working with the new View experience, please create enhanced variables instead.
Legacy Knowledge Model variables allows you to store a value centrally while referencing it in one or more other entities within the same Knowledge Model.
Legacy Knowledge Model variables can be referenced using the ${ } reference operator and use the following format:
(${variable_ID})Legacy package and legacy View variables
In addition to legacy Knowledge Model variables, you can also create and use variables in legacy packages and legacy Views. These other legacy variables are not interchangeable, so must be created and used independently.
Legacy package variables: Legacy package variables allow you to centrally create and manage information that is referenced and reused across your package, enabling you to update them in one location only. See: Variables.
Legacy View variables: Legacy View variables allow you to centrally create and manage information that is referenced and reused across components and assets, enabling you to update them in one location only. See: Legacy view variables.
Creating legacy Knowledge Model variables
To create legacy Knowledge Model variables:
Click Studio and then open the package containing the KM you want to create the variable for.
Open the KM, select Variables, and then click Create Variable.
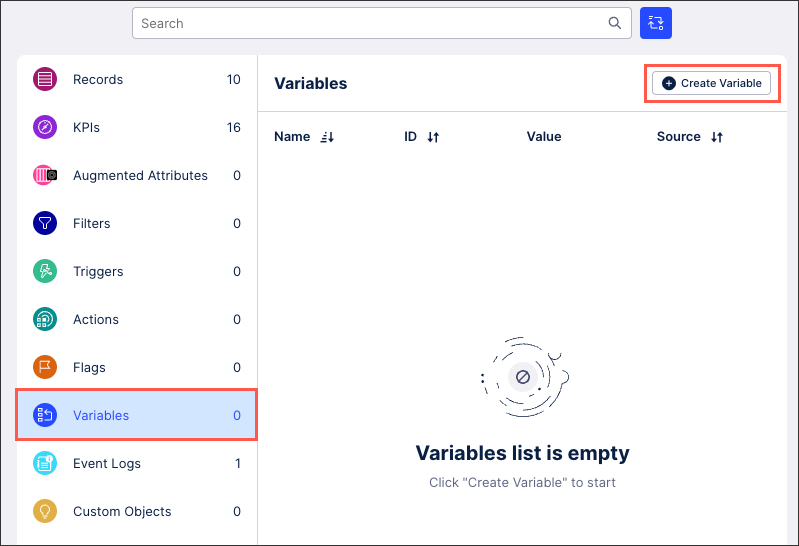
Configure your legacy KM variable using the following settings:
Display Name: A human-readable label used in the user interface.
Short Display Name: Shorter human readable label for the object shown automatically on the Views whenever the Display Name is truncated. Can contain max 20 characters.
ID: A unique technical identifier used to reference this variable. Must be unique within all attributes in the KM.
Description: A human-readable description for the variable.
Internal Note: A field only visible within the Knowledge Model.
Value: The default value to be used whenever this variable is referenced.
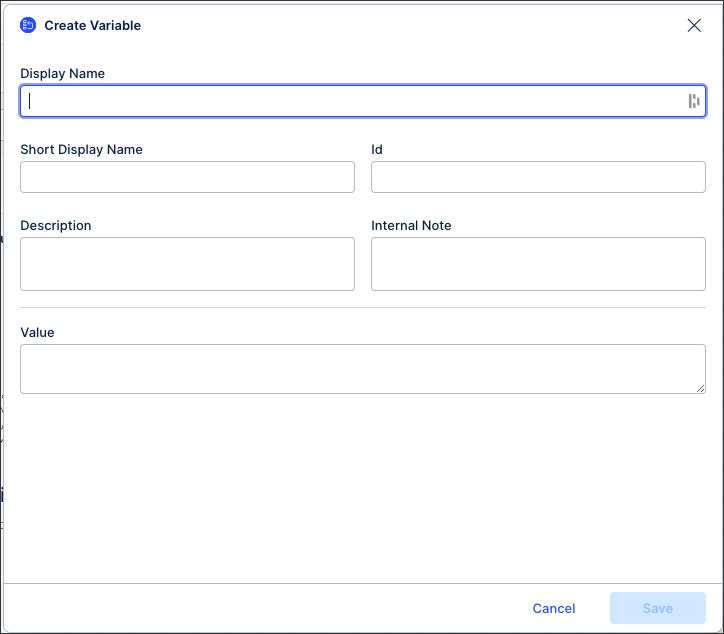
Click Save.
The variable is added to your Knowledge Model and available to use in your related content.
Managing existing Knowledge Model objects
Managing existing Knowledge Model objects
You can manage existing Knowledge Model objects by clicking the Options icon:
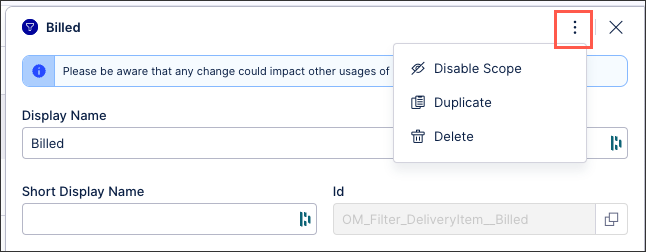 |
You then have the following options per object:
Disable scope: By disabling the scope of an object, the object then can't be used anywhere within the package. This is a good option if you want to disable an object but delete it from your KM.
Duplicate: This opens the create object window with the configuration of the object you are duplicating used as a template. When saving a duplicate object, the object ID must be unique.
Delete: This deletes the object from the KM and any references to that object in existing content. When deleting an object, there is no undo or recovery option.
Field name | Description | Required? | Expected value |
|---|---|---|---|
id | A technical identifier that is used for unique referencing | Yes | Alphanumerical, no spaces |
displayName | A human-readable label that is used in the user interface | Yes | String |
description | A human-readable description | No | String |
value | The variable value | Yes | Arbitrary |
Example
The following example shows a Variable definition that sets up a variable called 'LIMIT_ORDERS' which represents the maximum amount of orders. The Variable can then be referenced by name in any PQL field of the Knowledge Model using the Variable referencing syntax: ${LIMIT_ORDERS}. This makes maintenance of values easier which would be duplicated otherwise since the Variable can be managed in one single place.
- id: LIMIT_ORDERS displayName: Maximum amount of orders description: "" value: 500