Troubleshooting data extraction and pre-processing
If you used Celonis before object-centric process mining (OCPM), you may already have extractions set up. You can make this data available to the OCPM data pool by exporting the data connection from the source data pool and importing it into the OCPM data pool. See: Sharing data between data pools
If you plan to run case-centric and object-centric mining in parallel, we recommend using a single extraction data pool that holds all data connections and extractions, and feeding multiple transformation data pools—including the OCPM and case-centric ones. Export the data from the extraction data pool and import it into each transformation data pool.
If you’re not already using this setup, the move to OCPM is a good time to adopt it, as it reduces data duplication, APC usage, source-system load, and overall complexity.
To import data from an existing Data Pool to the OCPM Data Pool, follow these steps:
In your existing Data Pool, click on the context menu for the Data Connection (the three vertical dots), and select Share Data with other Data Pools.
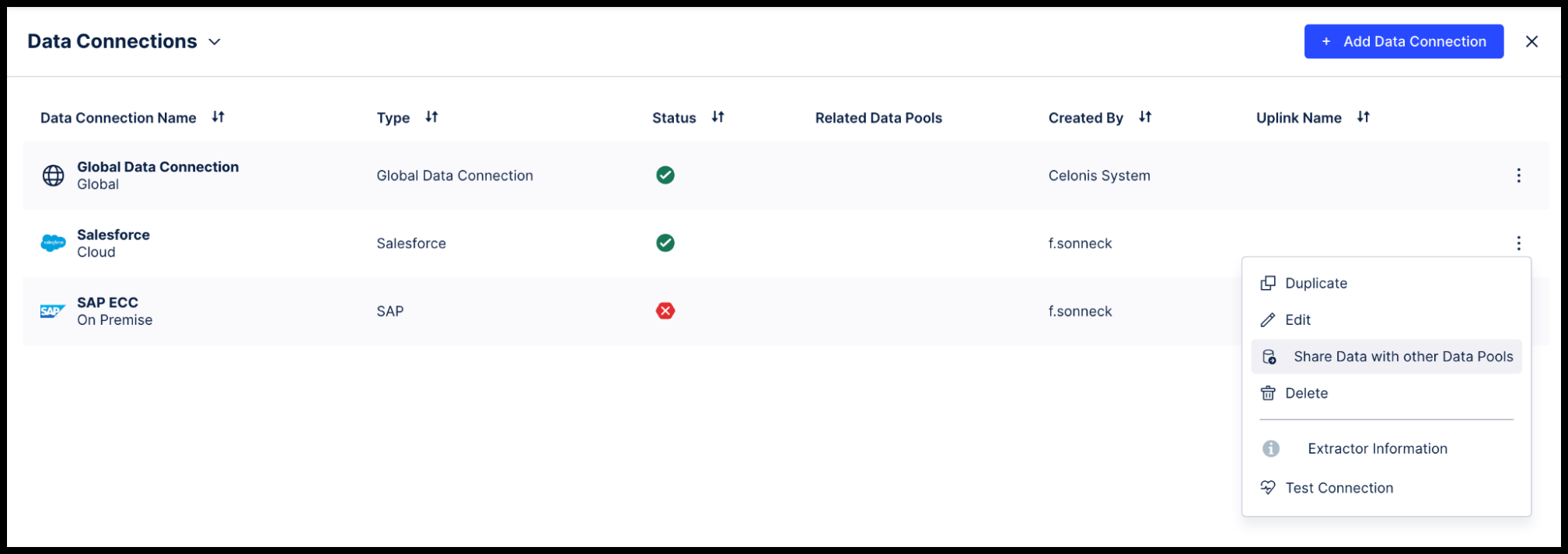
In the Share Data with other Data Pools window, select the OCPM Data Pool as the target, and share all the tables in the Data Connection.
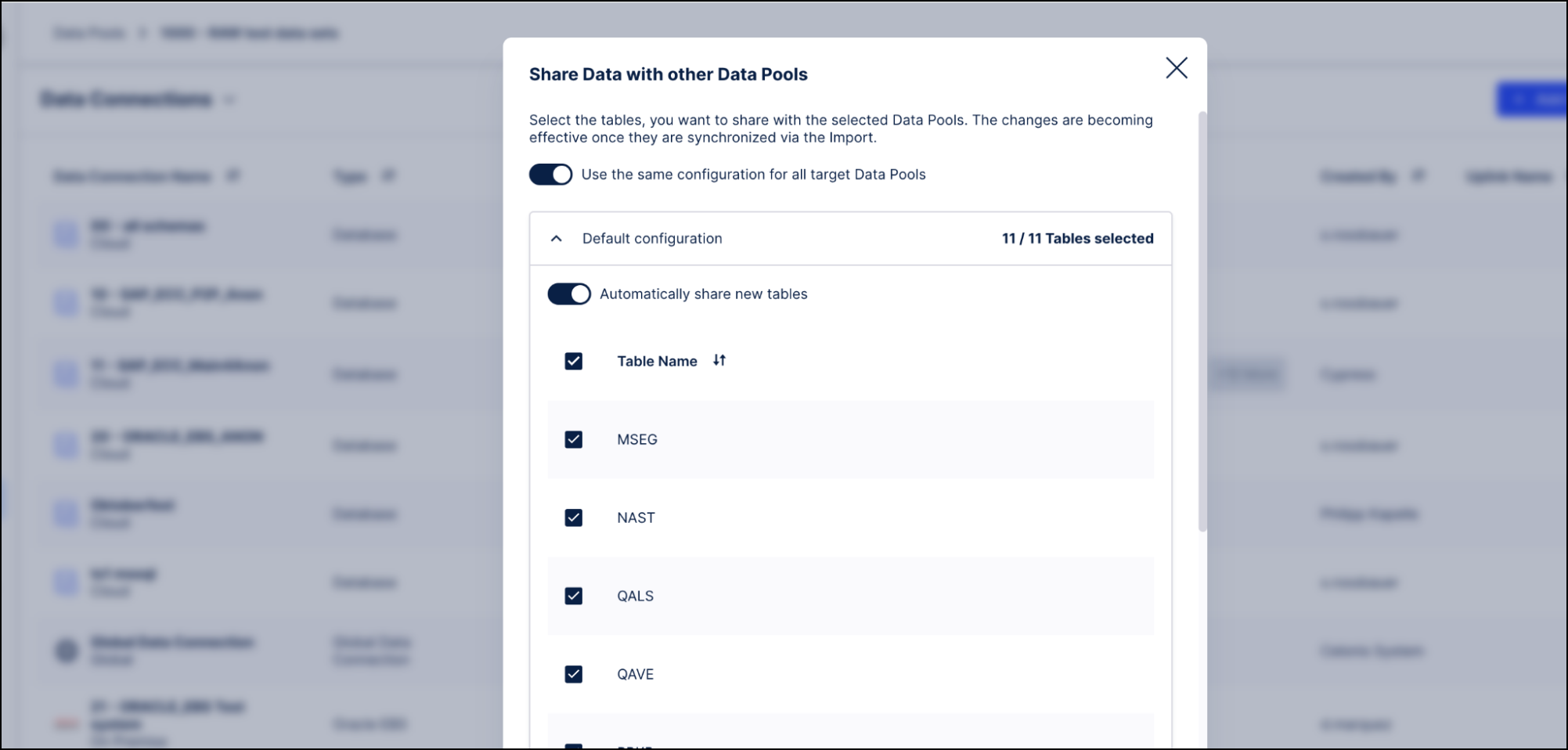
Go to the OCPM Data Pool, create a new Data Connection, and select Import data from another Data Pool. Select the Data Connection you have just shared and click Synchronize. The views are automatically created in the OCPM Data Pool.
Tip
You can’t export a Data Connection from the OCPM Data Pool and share it with another Data Pool, so this procedure doesn’t work the other way around.
Because you are importing the data to the OCPM Data Pool as views:
Changes to the data in the tables that you already shared from your existing Data Pool (for example, new records being extracted) are automatically reflected in the views in the OCPM Data Pool.
You’ll need to synchronize the import again if the structure of the shared tables changes, or if you add or remove tables from the Data Connection in the existing Data Pool. To pick up the changes, select the Data Connection in the OCPM Data Pool and click Synchronize.
Any SQL statements you run against the imported views in the OCPM Data Pool do not impact the tables in the existing Data Pool.
Your APC isn’t impacted by the views, which are essentially just stored SQL queries.
If you need to pre-process source data (filtering, type changes, renaming, etc.) but want to use Celonis’ supplied object and event transformations, keep the standard source table names. Using alternative names (e.g., TMP_BSEG instead of BSEG) requires creating and maintaining custom overwrites.
To pre-process while preserving standard names:
Create a dummy data connection in the OCPM data pool to open a pre-processing scope.
Build transformations in the global scope that read the source data and write views into the pre-processing scope with the same names as the original tables.
Apply your SQL pre-processing inside these view definitions.
Deploy the Celonis-supplied object/event transformations to the pre-processing scope so they run on your processed data.
Views keep the data dynamic and avoid APC usage, but heavy logic in views can slow downstream transformations. If you see performance issues in the ocpm-data-job, switch from views to tables in the pre-processing scope and run ANALYZE STATISTICS on them.
Setting up a dummy data connection
To set up the dummy Data Connection, follow these steps:
In Data Integration or from the Objects & Events dashboard, navigate to the OCPM Data Pool.
Select Data Connections.
Click Add Data Connection.
Select Connect to Data Source. The following steps work for SAP or Database - select whichever matches your context best.
Select an uplink (the status doesn’t matter here, as the uplink doesn’t have to be live) and click Next.
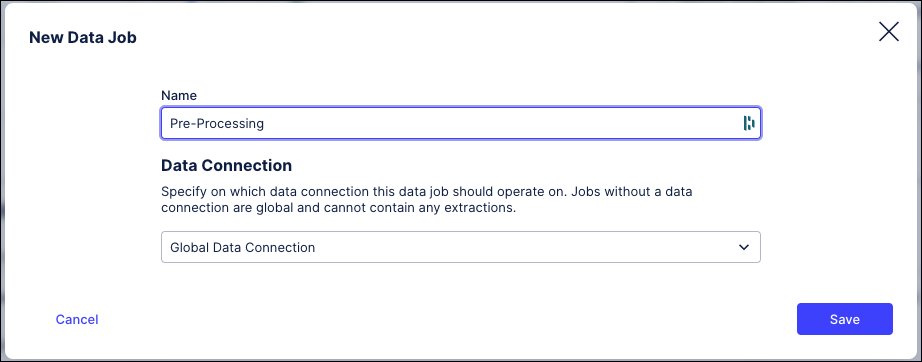
Give your connection a name - we’ve used “Pre-Processing”.
Insert dummy values for the remaining mandatory fields, as we’ve done in this example.
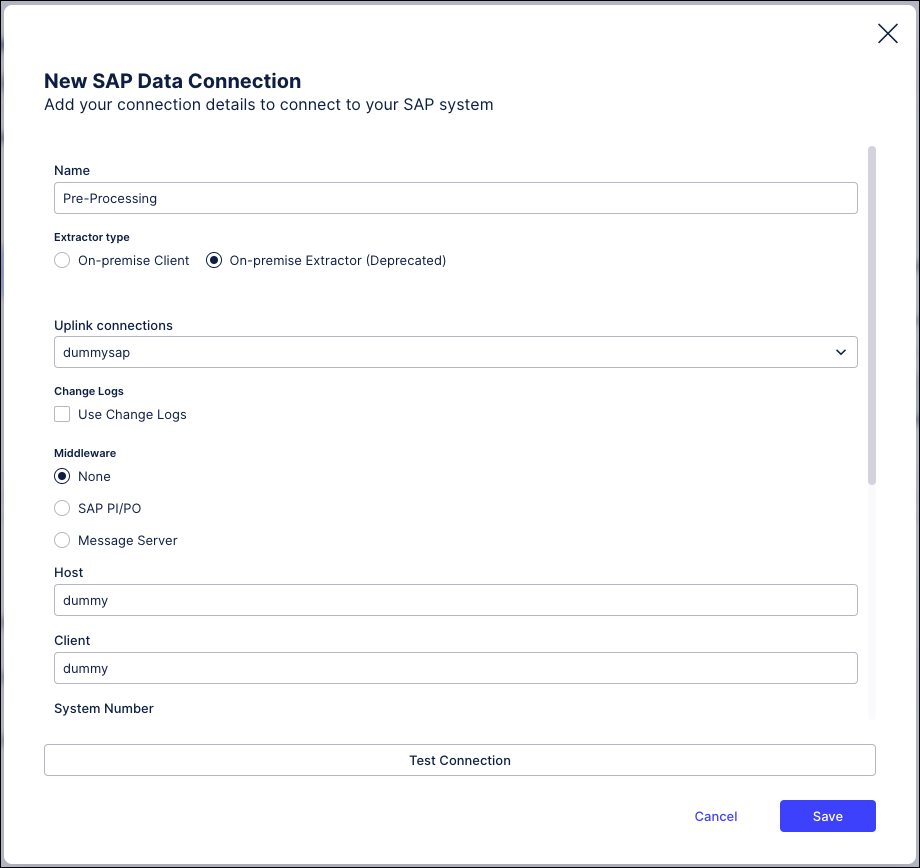
Click Save.
When you see the connection test error message ("Connection test failed, please check the Data Connector's configuration...") ,click Save Anyway. This isn’t a live connection.
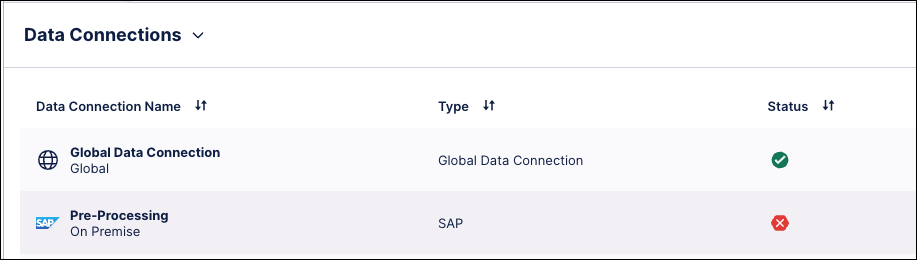
Check the connection overview for the OCPM Data Pool, and verify that the dummy Data Connection is present.
Creating the transformations that pre-process the data
To create the transformations that pre-process the data, follow these steps:
Create a new data job in the global scope of the OCPM Data Pool. You need to use the global scope because it is the only place with access to both the source data and the pre-processing scope.
For every view that you need in the pre-processing scope, create a transformation in the pre-processing data job containing SQL code based on the following template:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."TABLE"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."TABLE" AS ( SELECT * FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SOURCE_SCOPE%>."TABLE" );Give your views the same names as the tables in the source data. For example:
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PRE-PROCESSING%>."CDHDR"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PRE-PROCESSING%>."CDHDR" AS ( SELECT * FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SAP_ECC%>."CDHDR" );Add any pre-processing that you want to do for the data in each table, in the SELECT statement for the corresponding view, so that the view in the pre-processing scope will contain the pre-processed data. Here are some examples of pre-processing for common troubleshooting situations. You might also want to combine the different templates below.
Rename a table to the name expected by the Celonis transformations (see The table names or column data types in the extracted data differ from the SAP standard).
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."NEW_NAME"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."NEW_NAME" AS ( SELECT * FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SOURCE_SCOPE%>."OLD_NAME" );Convert a column data type to the type expected by the Celonis transformations, using CAST (see The table names or column data types in the extracted data differ from the SAP standard).
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF" AS ( SELECT MANDT, CAST(BUKRS AS VARCHAR), BELNR, GJAHR, ... FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SOURCE_SCOPE%>."BKPF" );Replace NULL values for a primary key (here, the accounting document number BKPF-BELNR) with an empty string, using the COALESCE() function. Don’t use ISNULL or IFNULL, as these functions are not supported for object-centric transformations. (See Error message: Cannot set a NOT NULL column (ID) to a NULL value in INSERT/UPDATE statement..)
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF" AS ( SELECT MANDT, BUKRS, COALESCE(BELNR,''), GJAHR, ... FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SOURCE_SCOPE%>."BKPF" );Include only data starting with the year 2023 in a view (see Creating objects and events for a limited data scope).
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF"; CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <%=DATASOURCE:PREPROCESSING_SCOPE%>."BKPF" AS ( SELECT * FROM <%=DATASOURCE:SOURCE_SCOPE%>."BKPF" WHERE GJAHR >= '2023' );
When you’ve created all the transformations, run the pre-processing data job to create the views in the pre-processing scope in the OCPM Data Pool, and verify that they contain the required changes.
In the OCPM Data Pool, schedule the pre-processing data job to run before the OCPM data job (ocpm-data-job).
To deploy the Celonis-supplied transformations for objects and events to the pre-processing scope, follow the steps in Quickstart: Extract and transform your data into objects and events, but in Stage 2 (Enable the processes you want), select your dummy Data Connection for the pre-processing scope, instead of the Data Connection for your source system. Then the Celonis-supplied transformations for the objects and events in the process will be deployed to the pre-processing scope and operate on your pre-processed data.
To limit your data scope (e.g., to one year) for performance or other reasons, you normally apply filters in the extraction. If you must keep extracting full tables to avoid impacting other use cases, restrict the data during pre-processing instead, using the method in Troubleshooting – Data Extraction – Pre-processing raw data (includes an example for filtering to 2023).
If no other use cases require the full dataset, simply filter the extraction directly in the OCPM data pool using the visual editor’s filter settings.
If your data comes from multiple source systems (e.g., SAP Spain, SAP Germany, SAP France, or different system types like SAP ECC and Oracle EBS), you can deploy the same process transformations for each source system. The OCPM data job (ocpm-data-job) then merges all source data into a single table per object or event type.
First, ensure all source tables are in the OCPM data pool. You can either set up a data connection for each system directly or export/import it from another data pool.
Once each data connection is in the OCPM data pool, install the required processes from the catalog for each connection. The data job merges all source systems’ data into unified tables for objects and events.
Celonis-supplied transformations need specific tables and columns. If you reuse a dataset created for case-centric processing, it may not include everything required.
When you publish the OCPM data job, Celonis adds transformation_initialize_source_tables to create empty placeholder tables for any missing ones required by Celonis-supplied transformations. This prevents failures, but placeholder tables contain no data, meaning objects and events based on them aren't created.
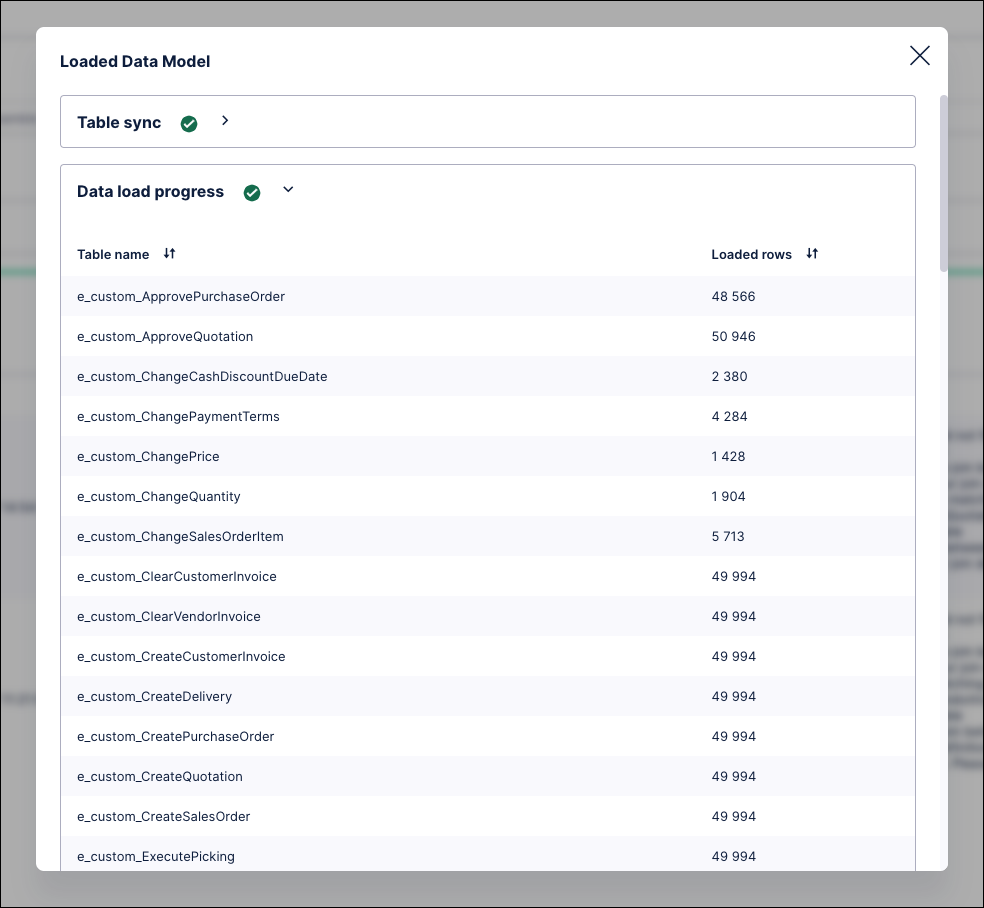
To see which objects and events are affected, open the Data Model load details and check the row counts. A count of 0 means no records were available. This transformation does not handle missing columns. If a required table is missing columns, its transformation will fail and indicate the first missing column. Update your extraction to include the missing fields.
The Celonis-supplied transformations from the processes in the catalog require the standard table names and column data types used in the source system. If your tables have had a prefix added to the table name (for example SAP_VBAK) or use an alternative table name, or if you have columns with nonstandard data types, there are several possible solutions:
Rename the tables or change the column data types during extraction. This is the easiest solution, but you can only do it if you aren't using the tables and columns for any other use case that requires the existing setup.
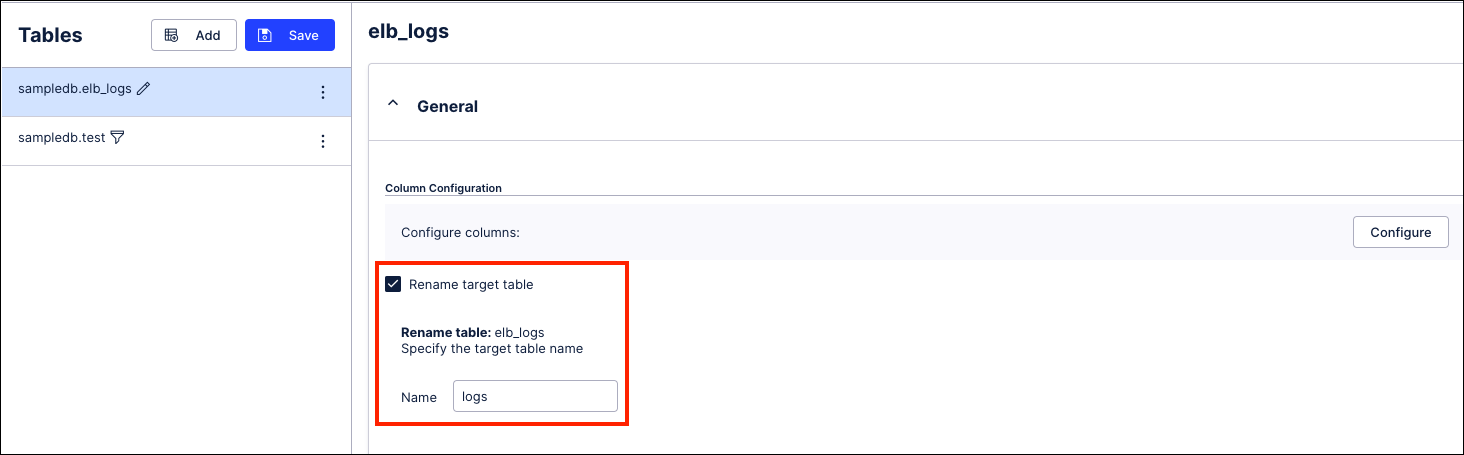
To rename a table, in the extraction configuration, select the checkbox Rename target table for any tables that need renaming, as shown in this example. Then carry out a full load to re-extract the table with the new name.
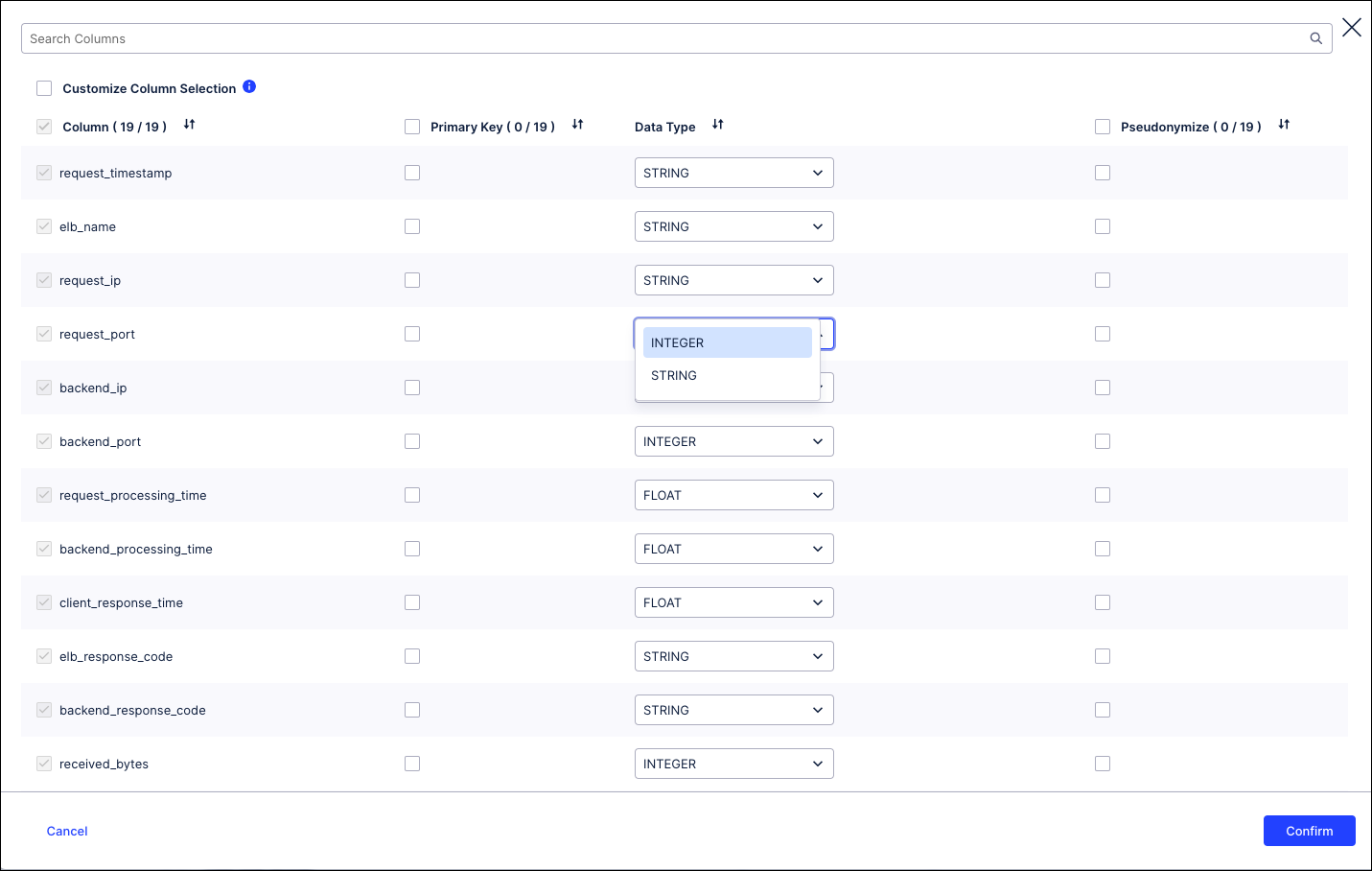
To change a column's data type, go to the extraction configuration where the table containing the column is defined, and click on the column configuration. Adjust the data types and click Confirm. Save the updated settings, then carry out a full load to re-extract the column with the new data type.
Note
Extractors don’t support all types of conversions. For example, you couldn’t convert a VARCHAR into a DATE. Also, not all extractors allow data type conversions at all. If you can’t do the conversion you want with the extractor you’re using, you’ll need to try one of the other solutions.
Rename the tables or change the column data types during a pre-processing stage. If you need to pre-process the data for other reasons as well, this is a convenient solution, and it works for shared tables.
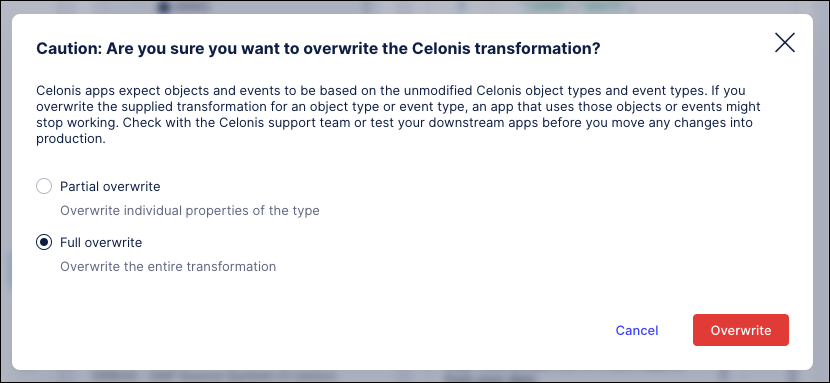
Create partial overwrites or full overwrites to replace the Celonis-supplied transformations. You can create a partial overwrite to change the definition of an individual column, or a full overwrite to change the name of a table.
Important
Creating a full overwrite of a transformation for a Celonis object or event type prevents it from receiving future updates from the Celonis catalog. New properties added to the object or event type will not be populated, and related apps may not function. If a full overwrite is used, you must manually track and apply future updates. Whenever possible, make changes during extraction or pre-processing instead.
Celonis-supplied transformations enforce primary keys. If a primary key column in the source data contains NULL values, the OCPM data job (ocpm-data-job) fails with an error such as: “ERROR: Cannot set a NOT NULL column (ID) to a NULL value in INSERT/UPDATE statement.”
To fix this, we suggest:
During table extraction, remove records with NULL values in primary key columns using the filter settings described in Creating extraction tasks using the visual editor. If these records are needed for your analysis, replace NULLs with empty strings or another placeholder to prevent transformation failures.
Replace NULL values during a pre-processing stage. This works well for shared tables and when pre-processing is needed for other purposes. Use the COALESCE() function to replace NULLs in primary key columns with an empty string. Avoid ISNULL or IFNULL, as they are not supported for object-centric transformations.
Create a full overwrite of the Celonis-supplied transformation to change the primary key or other settings. This replaces the original transformation entirely, but careful configuration is required to avoid unintended consequences.
Important
Full overwrites block future catalog updates; make changes during extraction or pre-processing whenever possible.
