Labeling Task Mining events
Task Mining Label overview
In Task Mining, adding labels as identifiers helps you organize and contextualize captured Task Mining events. There are two types of Labels:
Default Labels which are predefined for standard applications and are automatically applied to applications, screens and documents.
Custom Labels which you create and apply depending on how you want to organize your data.
Label rules apply Labels to event attributes. If an event attribute doesn’t have a default Label, it will display in your Task Mining data without a Label unless a rule applies a custom Label to it.
Note
When you create a Label, it is applied to new data only. However, if you re-process all the existing data, the Label will be applied to all data. For more information, see Task Mining data processing.
Task Mining label terminology
Term | Description | Additional information |
|---|---|---|
Default Label | Predefined label that uses a standard naming convention and is applied to event attributes for specific standard applications, screens and documents. Default Labels can be overridden by custom Labels. For more information about the standard applications that default labels are applied to, see Default labels for standard applications. | If event processing rules exclude certain events or applications, Default Labels will not be applied to excluded events and applications. |
Custom Label | User-defined label that is assigned to Task Mining event attributes. Can be used to override default Labels and be assigned to event attributes that don’t have a default Label. For more information, see Creating custom labels. Important Labels are not backwards compatible and cannot be applied to existing Task Mining projects. | Ensure custom Labels have unique, meaningful names that reflect the official full vendor name. Where software is available in both standalone and browser versions, both versions should have the same custom Label name. |
Label rule | Contains specific conditions that determine how and when a Label is applied during processing. | For default Labels, we’ve set up the label rules for you. For custom Labels, you define your own rules. For more information, see Creating custom labels. |
Attribute source | Where the label information originates from. | The attribute source can be:
Note Only attribute sources of type Label can be customized. For more information, see Task Mining attributes and label sources. |
Important
This table contains all the attributes that can be used as sources when labels are created, meaning they can be selected for conditions in label rules. For a full list of Task Mining attributes, see the Task Mining attribute reference.
Attribute | Attribute source | Description | Furcther information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Label | User-friendly name of the software application or website where the event occurred. By default uses the:
| For example, the standard Adobe Acrobat PDF Reader instead of Acrord32. |
| Label | Document name in applications that is predefined for standard applications and can be defined for other document types. | Users can group similar documents together using a Label. For example, you could create a Label called |
| Label | Screen name within an application. This is most useful for standard applications with many screens where screens have default Labels. If the application is focused on documents, for example in Excel, screens are not labeled as most time is spent on the main view which is the document. Grouping events using the | If a Label is defined for Using easy-to-understand screen names also helps when analyzing Task Mining data. For example, the Workday screen is defined by URLs like .workday.com/create-invoice/. so you could use a screen name of |
| Raw | Window name displayed at the top of every window and is generally the name of the application or website or further details. Taken from the window related to the user interaction event. | Configured in client settings and set by default to pseudonymize the Windows username. |
| Raw | Textual content stored in the Windows clipboard. | |
| Raw | Unique identifier assigned each time the clipboard content changes (EventType = 'Clipboard changed'). Used to count clipboard copy operations and to create a PQL domain table for tracking clipboard copy and paste actions in Studio. | Set to the event ID at the time of the change.All subsequent events within the same recording session share the same |
| Raw | Optional custom user attribute, like geographic region, that can be defined in the configuration file and applied by users. | For more information, see User Attributes. |
| Computed | Domain part of a URL where the raw event has a URL attribute.If the raw event has a URL attribute, the | For example, for URL https://www.google.com/search?q=test, the |
| Computed | Human-readable event description created by concatenating a number of attributes. | For example, in Gmail, this could be a left click on Send. |
| Raw | Event type:
| For more information, see the Event reference. |
| Raw | Command key or key combination. | |
| Raw | Visualizes the X-coordinate of the mouse pointer’s position in a screenshot. | A negative value indicates that the mouse pointer is outside of the screenshot. |
| Raw | Visualizes the Y-coordinate of the mouse pointer’s position in a screenshot. | A negative value indicates that the mouse pointer is outside of the screenshot. |
| Raw | Name of the application’s Windows OS process that was active when the user interacted with their machine. | Typically this is the ‘technical application name’, such as ‘saplogon’. |
| Raw | File name of the screenshot related to the event, if screenshots have been captured (optional). | |
| Raw | Unique ID of the Task Mining session where a session is the period of time from starting to stopping Task Mining. | Starting and pausing can be done by the user via the start/stop buttons or automatically depending on settings. |
| Raw | Windows user name of the active user who interacted with the computer. | Pseudonymized by default. For more information, see client settings. |
| Computed | Amount of time the user ‘spent’ on an event, calculated in seconds based on the timestamp of the next event minus the timestamp of the current event. | |
| Raw | When the event was detected in local time. | |
| Raw | When the event was detected in UTC. | |
| Raw | URL of the website that is currently opened in the tab that triggered the even | Availability depends on the application used. For more information, see Browser extensions overview. |
| Raw | Hashed Windows user name of the active user. | The value is hashed using SHA256. |
Default Labels for standard applications
Application name | Application URL | Application Label | Screen Label | Document Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Gmail | mail.google.com | Supported | Supported Example default Label values are | Supported |
Google Calendar | calendar.google.com | Supported | Unavailable | Not applicable |
Google Slides | slides.google.com/presentation | Supported | Not applicable | Supported |
Google Meet | meet.google.com | Supported | Supported | Supported Set to the meeting key. |
Google Drive | drive.google.com | Supported | Supported Example default Label values are | Not applicable |
Google Sheets | docs.google.com/spreadsheets | Supported | Not applicable | Supported |
Google Keep | keep.google.com | Supported | Not applicable | Unavailable |
Google Search | google.com/search | Supported for top-level domains | Unavailable | Not applicable |
Google Maps | maps.google.com | Supported | Unavailable | Unavailable |
Application Name | Application Label | Screen Label | Document Label |
|---|---|---|---|
Microsoft Teams | Supported | Supported | Not applicable. |
Microsoft Word | Supported | Not applicable. | Supported Name may sometimes contain non-document items such as Open when file open is active. |
Microsoft Excel | Supported | Not applicable. | Supported Name may sometimes contain non-document items such as Open when file open is active. |
Microsoft PowerPoint | Supported | Not applicable. | Supported Name may sometimes contain non-document items such as Open when file open is active. |
Microsoft Outlook | Supported | Supported | Supported Name may sometimes contain non-document items such as Open when file open is active. |
Microsoft OneNote | Supported | Unavailable | Unavailable |
Microsoft OneDrive | Not applicable. | Not applicable. | Not applicable. |
Application name | Application Label | Screen Label | Document Label |
|---|---|---|---|
SAP Logon | Supported | Supported | Supported |
Important
For SAP Logon, you must ensure some specific settings are enabled in the configuration file for your Task Mining project. For more information, see SAP integration.
Creating Custom Labels
In the Celonis Platform Navigation bar, select Data >Task Mining.
All available Task Mining projects open.
Open the project you want to create a custom label for.
In the Home page of your Task Mining project, select Labels
 .
.The Labels screen appears. Any custom labels that have already been created for your Task Mining project display here.
Select Create Label.
The Create Label screen appears.
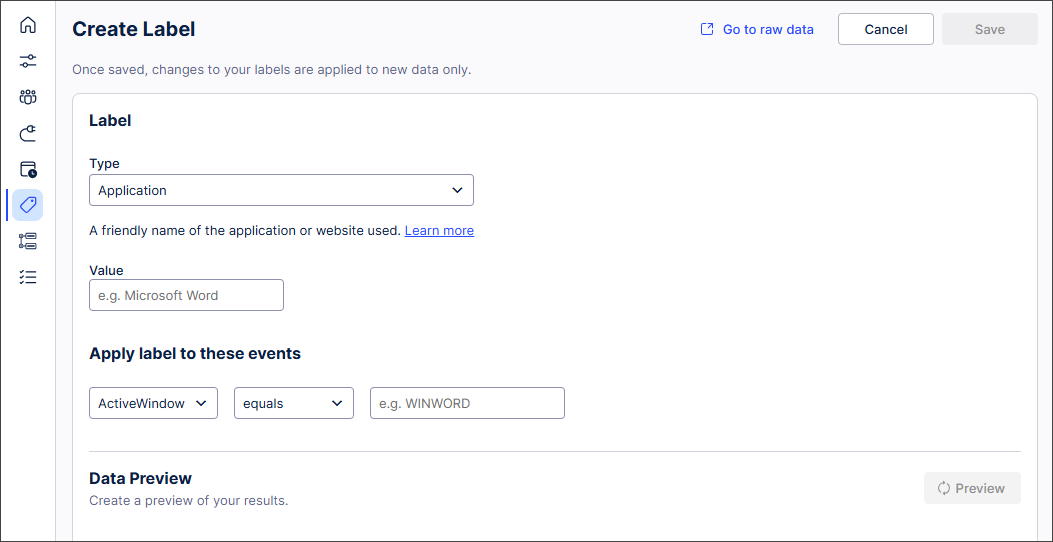
Complete the Label fields.
Tip
Select Go to raw data to view the events you might want to label.
In Data Preview, select Preview to see the raw events that will be labeled,
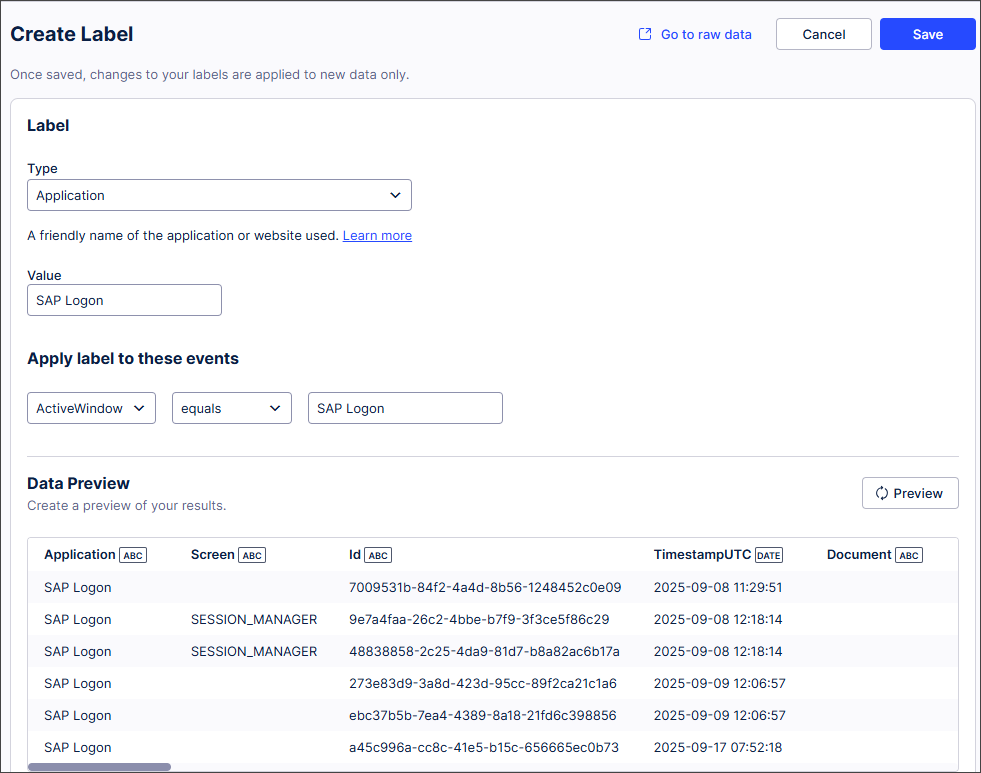
Note
If your data set is large, the Data Preview may not display. This is because Data Preview only looks at a limited amount of data (approximately 100, 000 events).
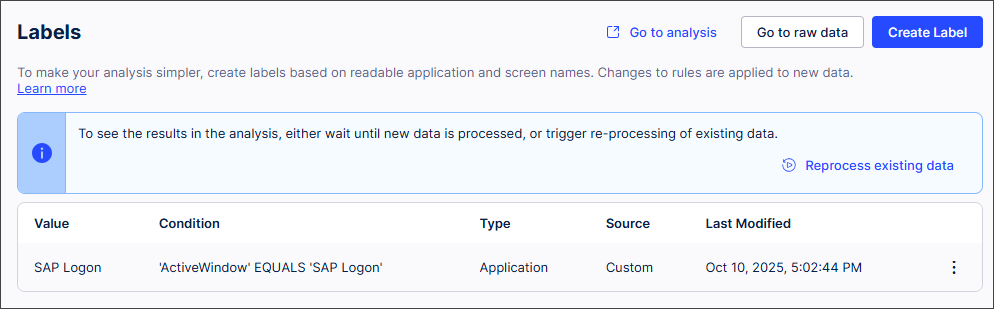
Select Save.
The Labels screen opens and displays the Label rule that is used to apply your custom Label.
Repeat steps 4 to 7 for each custom label you want to create
Custom Label fields
Section | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
Label |
| Defines whether the Label will be applied to an Application or a Screen. |
Label |
| The name of the Label. This should be user-friendly and easily identifiable. |
Apply label to these events | -- | Defines the custom rule that specifies when the Label should be applied. For example, you could create a custom rule like |
Editing and deleting custom Labels
In the Celonis Navigation bar, select Data > Task Mining.
All available Task Mining projects open.
Open the Task Mining project you want to edit or delete a custom Label for.
In the Home page of your Task Mining project, select Labels.
The Labels screen appears. Any custom Labels that have already been created for your Task Mining project display here.
Select the three dots next to the custom Label.
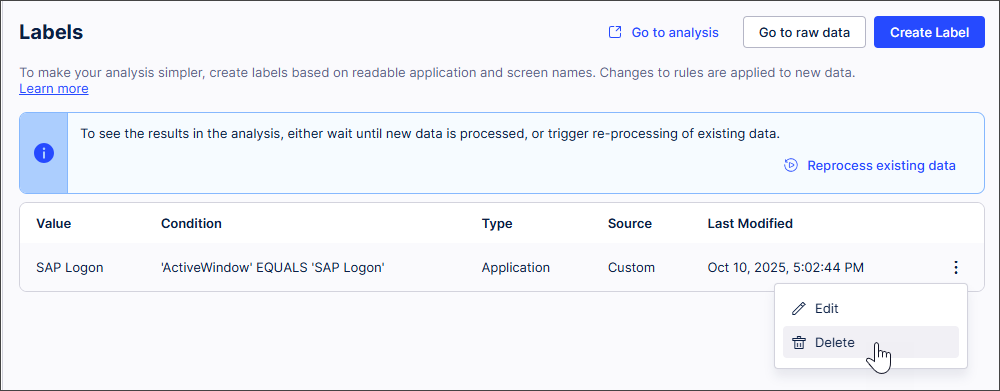
Select
Edit and make any changes required before selecting Save; or
Delete and confirm deletion when prompted.